 Mosquitoes are simply part of life in the late spring, summer, and early fall months. There are a wide variety of products on the market aimed at keeping mosquitoes at bay, including citronella candles, bug spray, and even wearable mosquito repellent. Mosquito bites are large and itchy, but they can sometimes be much more than just a nuisance.
Mosquitoes are simply part of life in the late spring, summer, and early fall months. There are a wide variety of products on the market aimed at keeping mosquitoes at bay, including citronella candles, bug spray, and even wearable mosquito repellent. Mosquito bites are large and itchy, but they can sometimes be much more than just a nuisance.
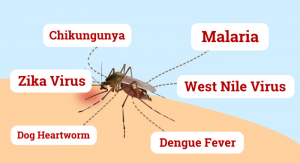
Mosquito bites can transmit serious and sometimes even fatal diseases, especially when they are not diagnosed and treated quickly. Understanding mosquito-borne illnesses and their symptoms can help you take the first step to protecting your home and family from these dangerous pests.
Chikungunya
While the Chikungunya virus, or CHIKV, is generally not deadly, the most common symptoms are a high fever that comes on suddenly and may be intermittent, as well as pain in the joints. Other, less common symptoms of this virus include swelling of the joints, a rash, headaches, and muscle pain. These symptoms can last for weeks and in some cases, even years. The virus was first discovered in 1952 in Tanzania.
Outbreaks of this virus have occurred mostly in countries outside of the United States, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and on islands in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. However, the Caribbean Islands have recently seen an outbreak of the Chikungunya virus and there is a concern that infected travelers may bring the virus deeper into the United States.
Dengue Fever
The Dengue virus is a particularly deadly type of mosquito-borne illness and over ⅓ of the global population is at risk for contracting this disease. Dengue fever is the leading cause of death in tropical and subtropical areas of the world, and approximately 400 million people contract the disease every year.
Symptoms of this virus include a high fever, accompanied by at least two of the following symptoms, such as severe pain behind the eyes, severe headache, rash, joint pain, muscle pain, low white blood cell count, and mild bleeding like nosebleeds or hemorrhaging in the eyes. The fever will begin to decrease in the first 3-7 days after the start of symptoms, and the disease is less severe in young children and individuals who are experiencing their first dengue infection. Vomiting, vomiting blood, breathing problems, pale or clammy skin, severe abdominal pain, and red blotches on the skin can be signs that the disease is worsening and requires immediate medical intervention.
No specific treatment exists for the Dengue virus and treatment includes symptom management.
Dog Heartworm
Heartworms are a common illness in dogs, but can be fatal in some cases where treatment isn’t immediate. This disease results in foot-long, thin worms that take up residence in a dog’s heart, lungs, and blood vessels. Heartworms can cause serious damage to these tissues, including heart and lung disease that result in the death of the dog. If the heartworm infection persisted for any length of time before treatment, there can be lasting effects to the health of the dog, even after the infection was eradicated.
Heartworms are transmitted when a mosquito feeds on an infected host and carries microscopic worms to another animal. Heartworms can take up to 6 months to fully develop after the initial bite. In the beginning of a heartworm infection, a dog may not show any symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, dogs can exhibit trouble breathing, lethargy, pale gums, and dark or bloody urine.
Heartworm can be prevented in dogs with a simple monthly medication, however, it is important to ensure that the dog is free of heartworms before the medication is administered.
Malaria
Malaria is another serious and sometimes fatal mosquito-borne disease. The United States sees approximately 1,500 cases of malaria every year, while other countries may see many more, especially in South Africa and Asia. Symptoms of malaria include shaking chills, high fevers, and general flu-like symptoms like nausea and body aches.
Only one type of mosquito — the Anopheles mosquito — can transmit the disease, which is usually carried when a mosquito feeds on an infected person and then again on a healthy person. Malaria cannot be spread from person to person and is only carried by the one specific type of mosquito, or through blood to blood contact, such as during a blood transfusion or sharing used needles for intravenous drug use.
A person with malaria may begin to feel sick between 10 days to 4 weeks following the initial infection, and may continue to feel sick for up to a year later. With prompt treatment, malaria is rarely fatal, with the exception of small children under the age of 5.
West Nile Virus
The West Nile Virus is another deadly mosquito-borne disease that can infect both animals and humans. The disease was first discovered in North America in 1999, and has spread across the entire U.S. and Canada. It has also been documented in other countries like Africa, India, Australia, and parts of the Middle East and Asia.
The virus is spread when a mosquito feeds on an infected bird and then bites a healthy human or animal. The virus is typically not spread through other blood to blood contact, but it has happened in rare cases. People who are infected with the West Nile Virus can incubate for 2-14 days after the initial mosquito bite, and most people do not exhibit any symptoms. Febrile illness, such as body aches, headaches, rash, diarrhea, and vomiting develops in about 1 in 5 infected people, and less than 1% of people infected with the disease will develop serious conditions like encephalitis (swelling of the brain) or meningitis.
Like with other mosquito-borne illnesses, medical treatment focuses on management of symptoms.
Zika Virus
The Zika Virus is a relatively new discovery, and has been reported in Northern areas of South America and Mexico. However, this virus has the potential to spread rapidly via mosquito bites. The CDC reports that the symptoms of the Zika Virus include red eyes (conjunctivitis), fever, joint pain, and a rash. In May of 2015, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) alerted authorities regarding an outbreak of Zika in Brazil, which proved to be more serious and resulted in more adverse effects to pregnant women and their babies. Overall, the Zika Virus is mild and only 1 in 5 people who are infected with the virus actually become ill. The symptoms only last a few days or up to a week. Very rarely is hospitalization required, and there are no medications or vaccinations available for Zika. Treatment generally includes rest, hydration, medications to reduce fever and inflammation, and testing for other mosquito borne illnesses that may be more serious, like Dengue Fever.
How to Protect Your Home and Family from Dangerous Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes can transmit very serious, and even deadly diseases if left unchecked. No longer are they seen as a normal summer annoyance, but instead, as the dangerous creature they are. Protecting yourself from mosquito bites is the best way to avoid contracting a mosquito-borne illness. Host family functions indoors or on a screened-in porch, and place mosquito netting around your bed if you live or travel to an area that is heavily infested with mosquitos. Use repellent when engaging in activities like camping, biking, or hiking.
A professional pest control company like Colonial Pest can help you eradicate mosquitoes from your home and yard, so you can still enjoy the warm weather outdoors without the threat of mosquitoes harming your family.